A denial-of-service attack aims to prevent access to a server or website. E-banking users can be affected, but also unwittingly involved in such attacks. Protect yourself!
Protect yourself against denial-of-service (DoS) attacks.
- Use up-to-date antivirus software.
- Monitor your Internet connection with the help of a firewall.
- Regularly install updates for your operating system and all software installed.
- Watch out and always remain alert.
There are different types of DoS attacks. The most common one consists of simultaneously sending out enormous quantities of data to a service located on a server, so that it becomes overloaded and is unable to reply to any further requests (the website is for instance no longer displayed in your browser). In general, no data are stolen or damaged this way.
Such large data volumes are usually send out with the help of a bot net. This is then called a distributed denial of service attack (DDoS attack - see below).
It is important you follow our “5 steps for your digital security” so that your device does not become part of a bot net and thus an “involuntary participant” in a DDoS attack.
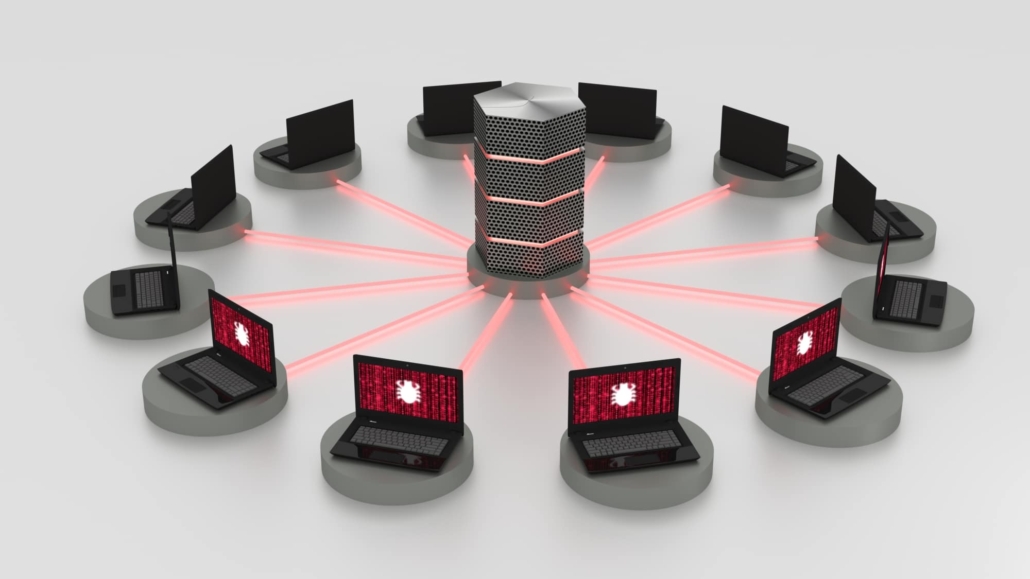
Co-ordinated attack originating from several devices
(DDoS – Distributed denial of service)
The most frequent type of DoS attack is a so-called Distributed Denial of Service attack (DDoS attack), which is run from a large number of coordinated devices simultaneously.
DDoS attacks are split into two stages. During the first stage, attackers bring several devices on the Internet under their control with the help of a Trojan or some other malware and then proceed to build them into a so-called bot net. During the second stage, the attackers will then take control of the infected devices (the bot net) and get them to attack the target (for instance a website) all at the same time.
A DDoS attack is very effective, since it takes place from several devices simultaneously, making it very easy to generate the great volume of data required. This method is mainly used to paralyse servers and websites. With DDoS attacks, it is difficult to establish the actual originator of the attack, since the attacker’s device does not itself attack the target.